3. Legal bodies responsible for regulatory procedures
| Site: | EUPATI Open Classroom |
| Course: | Regulatory procedures- Marketing-Authorisations and their lifecycle management |
| Book: | 3. Legal bodies responsible for regulatory procedures |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Wednesday, 9 July 2025, 1:32 AM |
1. Legal bodies responsible for regulatory procedures
(This section is organised in the form of a book, please follow the blue arrows to navigate through the book or by following the navigation panel on the right side of the page.)
In the EU, a medicine for human use may be authorised either by the European Commission through the centralised procedure or by national competent authorities through a mutual recognition, decentralised or national procedure:
|
Authorising body |
Procedure |
Scientific Assessment |
Territorial scope |
|
Commission |
European Medicines Agency (EMA) through its committees |
EU +EEA States Liechtenstein, Norway, Iceland |
|
|
National competent authorities |
National competent authorities |
EU countries concerned |
* These procedures are overseen by the Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA) via the Coordination Group for Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures (CMDH)
1.1. National competent authorities (NCAs)
The competent authorities of the Member States (MS) are responsible for the regulation of medicines which are placed on their markets via non-centralised procedures (national decentralised or mutual recognition) and that do not pass through the centralised procedure (see below).They also supply European experts who serve as members of the EMA's scientific committees, working parties or in assessment teams supporting their members. The national competent authorities, coordinate their work in a forum called Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA).
- When the MA is issued, the MA holder has to be informed by the NCAs about the approval of the summary of product characteristics (SmPC) having been agreed before between applicant and NCA(s) .
- The NCAs should make publicly available without delay the MA together with the SmPC (unless prohibited by national law)
- The NCAs have to provide an assessment report, and update it whenever new information of importance for the evaluation of the quality, safety or efficacy of the medicine becomes available
- A Public Assessment Report (PAR) in a version without commercially confidential information has to be publicly accessible together with the reasons for their opinion. It shall include a summary written in a manner that is understandable to the public. The summary shall contain, in particular, a section relating to the conditions of use of the medicine.
Legal Basis: Article 21, Directive 2001/83
1.2. European Medicines Agency (EMA)
The European Medicines Agency (EMA), established in 1995:
- underpins the centralised authorisation procedure and supports coordination between NCAs. The Agency is the hub of a European medicines network comprising over 40 national regulatory authorities.
- is a decentralised agency of the European Union acting as a networking organisation based in Amsterdam, whose activities involve thousands of experts from across Europe. These experts carry out the work of EMA's scientific committees
- facilitates development and access to medicines
- performs the scientific evaluation of applications for marketing authorisation under the Centralised Procedure (CP).
- supervises and monitors the safety of medicines in the EU across their lifecycle
- provides information to healthcare professionals and patients and publishes clear and impartial information about medicines and their approved uses. This includes public versions of scientific assessment reports and summaries written in lay language.
- has seven scientific committees*, six of which concerned with human medicines, that perform its scientific assessments and evaluate medicines along their lifecycle from early stages of development, through marketing authorisation to safety monitoring once they are on the market.
- has in addition a number of working parties and related groups which the committees can consult on scientific issues relating to their particular field of expertise
EMA’s scientific committees:
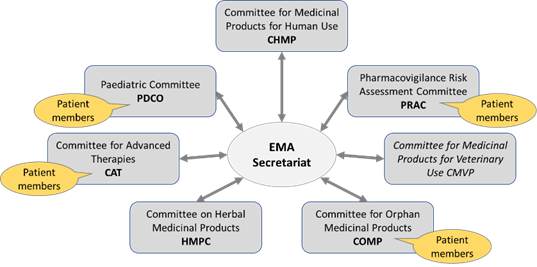
It may be of interest to also know what is NOT in the remit of EMA. The box below (adapted from the EMA website) contains those items which EMA lists as not falling under their activities.
What EMA does not do
- evaluate the initial marketing authorisation application of all medicines in the EU. For more information on medicine authorisation routes in the EU, see Authorisation of medicines;
- evaluate applications for the authorisation of clinical trials. The authorisation of clinical trials occurs at Member State level, although the Agency manages a database of clinical trials carried out in the EU.
- evaluate medical devices. Medical devices are regulated by national competent authorities in Europe. EMA is involved in the assessment of certain categories of medical devices. (e.g. an ingestible sensor that is incorporated into a medicinal product)
- evaluate food supplements and cosmetics. These substances are evaluated at national level;
- carry out research or develop medicines. Pharmaceutical companies or other medicines developers carry out the research and development of medicines, who then submit the findings and test results for their products to the Agency for evaluation;
- take decisions or have information on the price or availability of medicines. Decisions about price and reimbursement take place at the level of each Member State in the context of the national health system of that country;
- control the advertising of medicines. The control of the advertising of non-prescription medicines in the EU is primarily conducted on a self-regulatory basis by industry bodies, supported by the statutory role of the national regulatory authorities in the Member States;
- control or have information on pharmaceutical patents. Patents having effect in most European countries may be obtained either nationally, via national patent offices, or via a centralised process at the European Patent Office;
- develop treatment guidelines. National governments or the health authorities of individual EU Member States develop guidelines for decisions regarding diagnosis, management, and treatment in specific areas of healthcare (sometimes known as clinical guidelines);
- provide medical advice;
- develop laws concerning medicines. The European Commission develops EU legislation concerning medicines and the European Parliament together with the Council of the European Union adopt it. The European Commission also develops EU policies in the field of human or veterinary medicines and public health. For more information see European Commission: Medicinal products for human use;
- issue marketing authorisations. The legal decision to grant, suspend or revoke a marketing authorisation for any medicine falls under the remit of the European Commission for centrally authorised products, and the national competent authorities of the EU Member States for nationally authorised products
1.3. Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA)
The HMA is a network of the Heads of the National Competent Authorities coordinated and supervised by a Management Group. The HMA is supported by working groups covering specific areas and a Permanent Secretariat.
The HMA work closely with the EMA and the European Commission to maximise cooperation and ensure the European medicines regulatory network functions efficiently.
The HMA:
- addresses key strategic issues for the network, such as the exchange of information, IT developments and sharing of best practices
- focuses on the development, co-ordination and consistency of the European medicines regulatory system
- ensures the most effective and efficient use of resources across the network. This includes developing and overseeing arrangements for work-sharing between different regulatory authorities
- co-ordinates the mutual recognition (MRP) and decentralised procedures (DCP).
Member agencies support the network by providing high-quality professional and scientific resources to all areas of medicines regulation including centralised, MRP, DCP and national procedures.
Further information: http://www.hma.eu/
1.4. Coordination Group for Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures (CMD(h))
The CMD(h) is an HMA working group responsible for a smooth functioning of the mutual recognition and the decentralised procedures for human medicines and is responsible for the coordination of any scientific/regulatory issue related to these products.
It has particularly been set for the examination of any question relating to a MA, pharmacovigilance or variations of a medicine in two or more MS in accordance with the mutual recognition or the decentralised procedure.
Applications for a mutual recognition or a decentralised procedure which are submitted to the NCAs involved in the procedure are overseen by the CMD(h).
The Group also deals with issues related to national procedures when needed. For example, when the same product is authorised in different countries through the national procedure (before the MRP was mandatory) and requires any action related to harmonisation, safety, etc.
Further information: http://www.hma.eu/cmdh.html
Article 27, Directive 2001/83/EC